Abstract
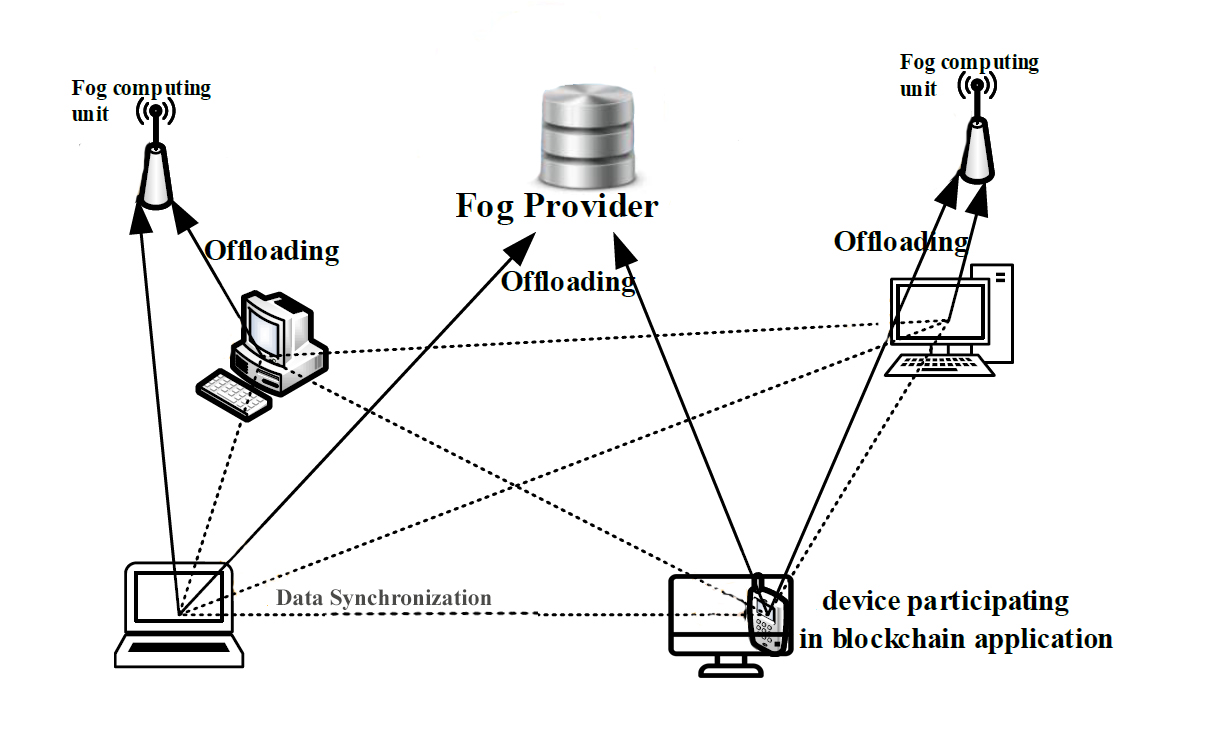
To meet latency constraints, fog computing takes computational assets to the network edge. Blockchain and reinforcement learning are increasingly being integrated into the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) to enhance security and efficiency. This study introduces a Reinforcement Learning-based Resource Scheduling Approach for Blockchain Networks in IIoT. Unlike previous studies, which mainly focus on either blockchain security or resource allocation, our approach integrates reinforcement learning for dynamic resource scheduling, improving efficiency while minimizing latency. The methodology is illustrated through a flowchart. Simulation results validate the effectiveness in multiple scenarios. Future work includes enhancing inter-node communication reliability.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Garg, M. (2025). Enhanced Reinforcement Learning-Based Resource Scheduling for Secure Blockchain Networks in IIoT. IECE Transactions on Machine Intelligence, 1(1), 29–41. https://doi.org/10.62762/TMI.2024.529242
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue