Abstract
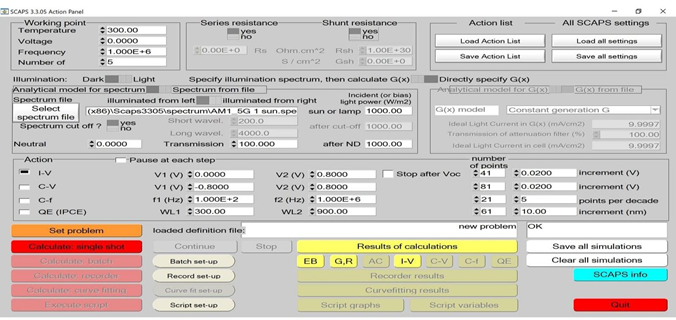
This study aims to computationally investigate the role of WS2 as an electron transport layer (ETL) and CuI as a hole transport layer (HTL) in optimizing the performance of perovskite solar cells (PSCs). The novelty lies in systematic optimization of band gaps, layer thicknesses, and temperatures to achieve enhanced performance metrics, utilizing the unique properties of WS2 and CuI, which are less explored compared to conventional materials like TiO_2 and Spiro-OMeTAD. The optimized PSC configuration achieves a power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 20.71% with a fill factor (FF) of 71.80%, an open-circuit voltage (Voc) of 0.8469 V, and short-circuit current density (Jsc) of 34.06894 mA/cm^2 under standard conditions.
Keywords
perovskite solar cells (PSCs)
electron transport layer (ETL)
hole transport layer (HTL)
WS2 (tungsten disulfide)
power conversion efficiency (PCE)
band gap optimization
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Bibi, N., Qasim, I., Seemab, N., & Mushtaq, B. (2025). Computational Study to Explore the Role of WS2-ETL and CuI-HTL in the Optimized Performance of Perovskite Solar Cell. IECE Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control, 2(2), 95–105. https://doi.org/10.62762/TSCC.2025.859391
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue