Abstract
Deep learning models are pivotal in the advancements of Artificial Intelligence (AI) due to rapid learning and decision-making across various fields such as healthcare, finance, and technology. However, a harmful utilization of deep learning models poses a threat to public welfare, national security, and confidentiality. One such example is Deepfakes, which creates and modifies audiovisual data that humans cannot tell apart from the real ones. Due to the progression of deep learning models that produce manipulated data, accurately detecting and classifying deepfake data becomes a challenge. This paper presents a groundbreaking IRV2-Hardswish Framework for deepfake detection, leveraging a hybrid deep learning architecture that synergizes residual blocks in CNNs and the Inception-Resnet-v2 model. By incorporating residual blocks to capture underlying audiovisual data layers and enhancing Inception-Resnet-v2 with Hardswish activation for robust feature extraction, our framework achieves accurate detection of deepfakes. Furthermore, additional dense layers are integrated to ensure precise classification, establishing a comprehensive and effective solution for deepfake detection. Further, a detailed comparison of our framework with the state-of-the-art CNN models reports that our framework outperforms with 98% accuracy, 96% precision, and 95% AUC using the Deep Fake Detection Challenge (DFDC) dataset. The DFDC dataset is the largest, consisting of approximately 5,000 clips, including 1,132 actual and 4,118 false ones. The results report the efficiency of the proposed framework. These results demonstrate the framework's effectiveness in deepfake detection.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Akhtar, F., & Mahum, R. (2025). IRV2-hardswish Framework: A Deep Learning Approach for Deepfakes Detection and Classification. IECE Journal of Image Analysis and Processing, 1(1), 45–56. https://doi.org/10.62762/JIAP.2025.421251
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
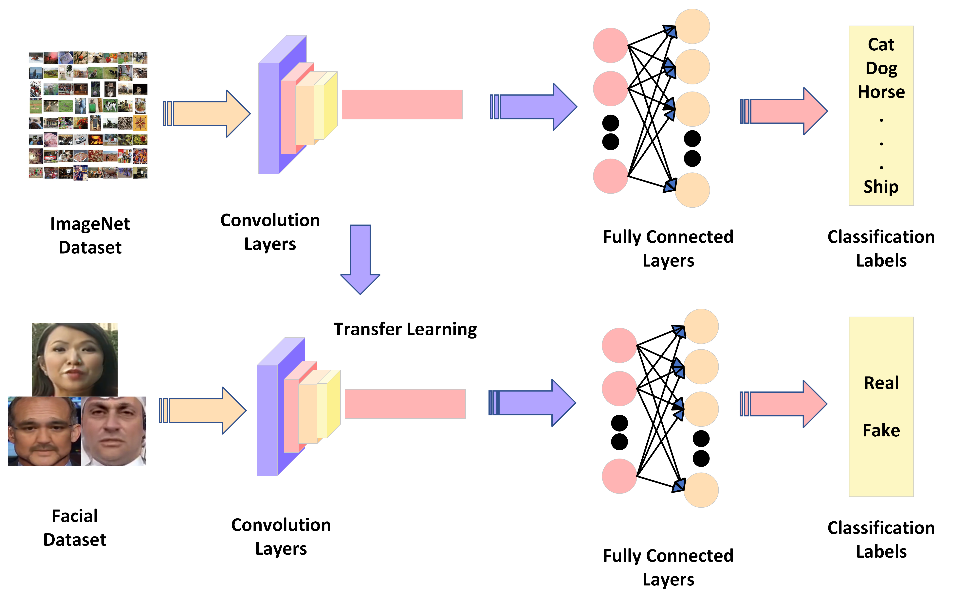
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 