Abstract
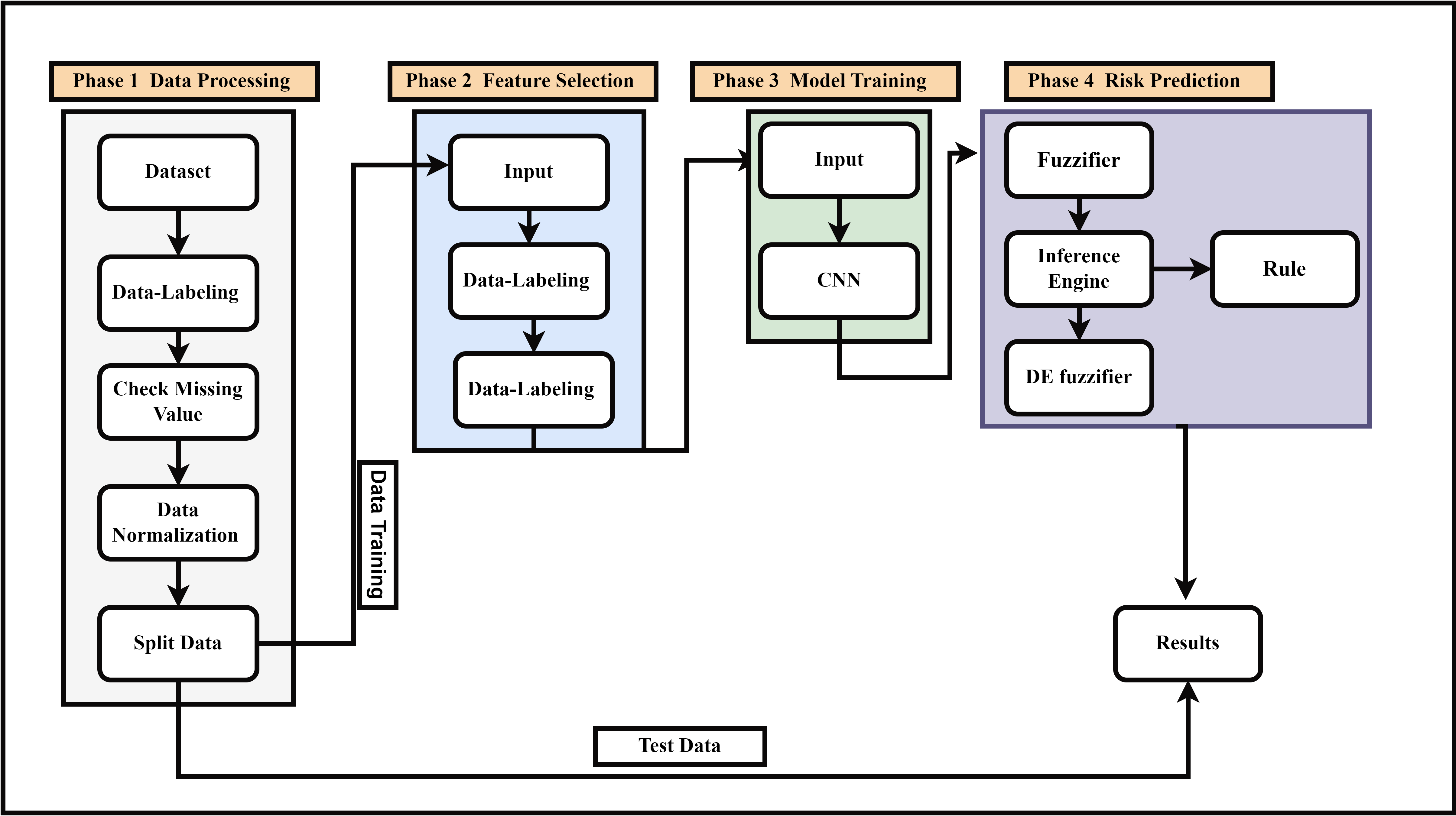
Across the globe, heart diseases rank as the top cause of death, with their incidence steadily rising. However, early detection before a cardiac event (e.g., cardiac arrest) remains a significant challenge. Although the healthcare sector possesses extensive data on heart disease, the effective use of this data for timely detection is essential to protect from such events. This paper proposes an innovative approach using fuzzy logic (FL), convolutional neural network (CNN) models, and feature selection to more accurately assess the risk of heart attacks. Our study also emphasizes the importance of data preprocessing, including data transformation, cleaning, and normalization, to facilitate the availability of trustworthy and high-quality information for analysis. We employed lassoCV for feature selection to identify key factors contributing to heart attack risk. Furthermore, we developed a novel 1D Convolutional Neural Network (1D-CNN) especially tailored for linear data to improve neural network training and the significant potential of advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques in revolutionizing heart attack risk estimation. We used fuzzy logic (FL) to handle data uncertainties in the risk prediction phase, enhancing prediction accuracy. Our proposed model achieved remarkable performance metrics: an accuracy of 98.5%, 100% precision, and 98.5% F1-score, which outperforms when compared with its counterparts.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Shafiq, S., Akbar, W., Hussain, A., Hussain, T., Soomro, A., Khan, I., Haq, M. I. U., & Adnan, F. (2024). FuzzDL-HeartPredict: Heart Attack Risk Prediction using Fuzzy Logic and Deep Learning. IECE Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems, 1(2), 63–77. https://doi.org/10.62762/TACS.2024.794425
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions

Copyright © 2024 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2024 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2024 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
