IECE Transactions on Social Statistics and Computing
ISSN: 2996-8488 (Online)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
By 2021, the efforts of the entire Party and people of all ethnic groups had completed the first centennial goal and embarked on the new journey toward the second century. The new generation of young people in China, born at a critical time, carries great responsibility. They are the driving force behind the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation and social progress, the successors to the cause of the Party and the country, and an important pillar in realizing the second centennial goal [1].
With the passing of time, more than a hundred years ago, tens of millions of Chinese youth bravely shouldered the burden of national rejuvenation amidst the turmoil of war. Today, the university students of the 2020s should draw strength from the spirit of struggle over the past century and fight for the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation. To achieve the next century's goals, we must move forward resolutely. Meanwhile, the arrival of the new century offers more entrepreneurial and employment opportunities for university students, though these opportunities are accompanied by numerous difficulties and challenges. However, a truly meaningful life cannot be solely determined by careers aimed at personal survival. The youth of the new era should integrate personal careers with national causes, take responsibility, and strive to realize their self-worth while fulfilling their historical mission and embracing the heavy responsibilities of the times.
Employment is the foundation of people's lives. As China's economic growth slows, the employment pressure on university students is also increasing, and stabilizing growth and ensuring employment have become key macroeconomic goals. Currently, the overall employment situation in China is good, but there remain many problems and challenges. With the expansion of higher education, an increasing number of university students are graduating. As a large employment group, how to address the employment issues of university graduates has been a focus of China's employment policy and a central issue in academic research.
This study uses Citespace software to systematically analyze academic literature on the historical mission and hot topics concerning university students in the new era over the past decade. The goal is to address the most pressing issues concerning students and provide references for related policies and academic research. The knowledge map of keywords from 2011-2021 is illustrated, where the Q value = 0.79 (>0.3) and S value = 0.86 (>0.5), indicating ideal clustering results with high reference value. Due to the potential overlap and repetition of information across clusters, qualitative analysis was used to further integrate the clustering results. The findings reveal the following characteristics of employment research in the past decade:
The background of the study emphasizes the new era context [1]. The new era, as defined by the 19th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, marks a new period in the development of socialism with Chinese characteristics. Today, China faces new opportunities and challenges, with the principal contradiction evolving into "the contradiction between people's growing needs for a better life and the unbalanced and inadequate development." The employment issues of university graduates have shifted focus from employment rates to improving employment quality.
The scope of research has gradually expanded. The issue of university student employment not only highlights problems in higher education methodologies but also reflects the complex social factors behind them. Research on this topic spans phenomenological and interpretivist approaches, including current surveys and causal analyses of student employment capabilities, pressures, and other related issues. In this paper, we use Citespace to analyze and organize the main keywords of college students' development, as shown in Figure 1 high-frequency keyword information analysis map.
| Serial Number | Region | Political Status | Education | Discipline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AY03 | Guangxi | Party Member | Bachelor | Social Science |
| AY05 | Non-Guangxi | Party Member | Bachelor | Social Science |
| AY08 | Guangxi | Non-Party | Postgraduate | Natural Science |
| AY11 | Guangxi | Party Member | Bachelor | Social Science |
| BX06 | Non-Guangxi | Non-Party | Bachelor | Social Science |
| BX12 | Guangxi | Party Member | Bachelor | Social Science |
| BX19 | Guangxi | Non-Party | Bachelor | Natural Science |
| BX21 | Non-Guangxi | Party Member | Bachelor | Social Science |
| BX22 | Guangxi | Non-Party | Postgraduate | Natural Science |
| BY14 | Guangxi | Party Member | Bachelor | Social Science |
| AY22 | Guangxi | Non-Party | Bachelor | Social Science |
| BX28 | Guangxi | Party Member | Bachelor | Natural Science |
| BX29 | AY22 | Avesculate | Discipline | Discipline |

Using Citespace's TimeZoneView, the changes in the research on university student employment issues over time can be shown, as illustrated in Figure 2. The following trends are evident: to change students' employment attitudes, their perspectives on employment must first be altered. Keywords such as "employment situation," "employment value," "career identity," "labor force," and "talent cultivation" have closely related meanings in the academic discourse on employment attitudes. Research indicates that students' employment psychology significantly impacts their employment rate and quality. For instance, unclear career goals and issues of career identity contribute to challenges in adapting to job positions, creating a structural mismatch between talent supply and demand.
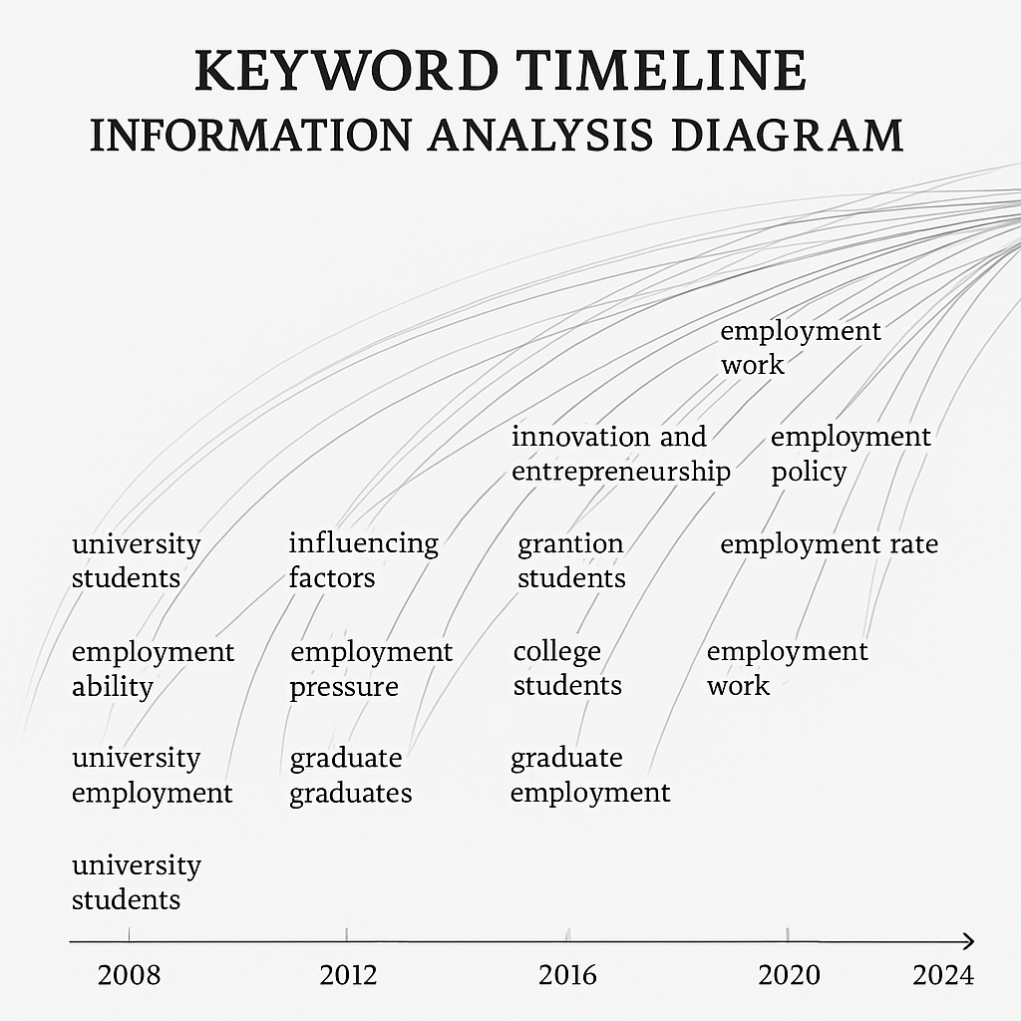
To explore the new normal of preferences in the historical mission and employment choices of university students from a social psychological perspective [5], the research team conducted interviews with 150 students, including 78 from 985 and 211 universities (coded as A), 72 from non-985/211 universities (coded as B), 73 male students (coded as Y), and 77 female students (coded as X). The survey included students from Guangxi (79) and other provinces (71), party members (77), non-party members (73), undergraduate students (82), and master's students (68). The basic characteristics of the participants are detailed in Table 1.
Due to the pandemic, interviews with students from Guangxi were conducted offline, while interviews with students from other regions were conducted online. The interviews explored topics such as job search channels, employment goals, and career expectations. The data were analyzed using Nvivo software. The students' employment mindset features were extracted and categorized into five core categories: "steady progress," "indifference," "balance," "doubt," and "self-satisfaction."
At present, college students are wandering between "ideal pursuit" and "realistic needs", but generally show a preference for "reality is more important than ideals", and present a "stable" trend in choosing careers. "Stable" trend in choosing career. The survey found that students' preferences for the goals of "salary and benefits", "settlement policy" and "work-life balance" were higher than their preferences for the goals of "playing up hobbies and interests" and "matching the right job". "The most typical preference is for "institutionalization". The most typical is the mentality of "system preference", in which students' willingness to choose to work in government agencies, public institutions, and state-owned central enterprises is significantly higher than that of foreign enterprises, private enterprises, and entrepreneurship. The overall preference for the ideal employment unit target of "within the system" has also gradually shifted from "civil servant fever" to favoring "the most important weapon of the state" and institutions, with 31 students (52%) Of the 31 students (52%) who explicitly expressed their willingness to enter the "system", 22 (37%) chose institutions or state-owned enterprises. (BX06) As for employment outside the system, students preferred large and medium-sized enterprises as a whole. (AY06) At the same time, the degree of willingness to work for foreign enterprises decreased significantly, and the willingness to work for private enterprises increased. (BY09) Further comparison reveals that female students are more willing to choose to work in the system than male students; students with relatives working in the system are more willing to choose to work in the system; party members are more inclined to work in the system than non-party members; college students who grew up in rural areas are more inclined to work in government organizations than those who grew up in urban areas; students with higher technical skills, such as foreign languages and computers, are more inclined to work outside the system; and students who have higher technological ability, such as foreign languages and computers, are more inclined to work outside the system than those who grew up in rural areas. , are more inclined to work outside the system.
At present, many college students hope to make finding a job easy and simple through ready-made resources such as state policies, and there exists the idea of dependence. Interviews found that close to 30% of students said that social relations played a more important role in finding a suitable career. "We would go to the briefing sessions in advance because the counselors would inform us in advance." (BY22) "I think the most effective way to find a job is to have a centralized job fair at school." (AY12) "Why do you need to work hard on your own if you have connections, besides, it's already difficult for girls to find a job, especially for us engineering majors who have to rely on some connections at home." (BX08) Further analyzing the emergence of this "lying down" mentality, the main manifestations are: First, the "command dependence" of the employment policy. Many students hope that the state can directly introduce relevant policies to ensure their own employment, but also hope that others can help them quickly and smoothly find their favorite jobs. For example, they hope that the school can really recommend employment enterprises, hope that the tutor directly give cases, and even some want to directly let the teacher help to submit resumes. "I think the school can give us resume templates so we can just fill in the information in without having to think hard." (BY24) "Career guidance courses may not be that useful, I think the school can contact companies directly and pass our information to them." (BY18) To the management of enterprises, students also boldly put forward their ideas, such as wishing to shorten the recruitment cycle according to their wishes, adjusting the time of interviews, as well as wishing that the interviewer could give a clear reply. Secondly, "geographical dependence" in the choice of employment area. The survey found that students gave priority to "more luxurious and fast-developing cities", "cities in the north", "second-tier cities with convenient transportation", "cities where they graduated from universities" and "cities where they have worked for a long time". The survey found that students preferred "more luxurious and fast-developing cities", "north to Guangzhou", "second-tier cities with convenient transportation", "city where they graduated from university", "home town", etc. "I feel that I should be able to find a better job in Guangdong, and Guangdong is a big city, so the future development prospect must be very good. " (AY10) "I'll look for a job in Beijing first, I'll have more face when I tell others, and if I can't find one, I'll go back to my hometown to look for a job." (AX07)
Contemporary college students have solidified thinking when choosing a career, but they also have innovative and advanced ideas. They want to make better development in their future positions, and hope that their career aspirations can be compatible with the outside world. Thinking about their future employment choices, they consider both their own values and external factors. The interviews reflect the reality that college students are willing to actively present their true selves when applying for jobs and strengthen their sense of identity, and at the same time, they also want to be recognized by others. College students also show a strong friendly and tolerant attitude when facing inconsistent suggestions. They have the idea of realizing their own value and pursuing themselves, but also consider the interests of others, respect the different ideas of others and try to solve disputes harmoniously. Due to the existence of such ideas and attitudes, in the employment decision-making into the embarrassing situation of not knowing how to choose, college students often fall into conflict, entanglement and even avoid thinking attitude. "I got an offer from a company with pretty good strength, and and what I studied is also in this area, the position is also what I prefer, but my parents want me to go to graduate school, graduate students out of the development prospects will be greater, I think what my parents said also has a point, I really don't know how to choose." (BY17) "I quite want to continue to work in this company, I have my own unique way of learning about this area of technology, but I heard my schoolmates say that this position doesn't have good development prospects, so I'm very torn." (AY02) In the face of career choices, college students often feel panicked if they don't follow the crowd, and feel that they don't have the enthusiasm to work because they don't have the personality. Many students in the interviews had dilemmas such as "being questioned about their career choices by people around them", "hoping to find a job with high development potential, but popular careers are very competitive", and felt anxious and uneasy. "Now I'm a little bit doubtful about my choice, I've received an offer from a company with a good salary, but other students in our major didn't choose this position, and I don't know if I've made the right choice." (BY20)
In today's world, technology is the dominant factor, while talents are an important resource for national development. With the deepening of global multipolarity and economic globalization, competition among countries is becoming more and more intense, and competition among countries is becoming more and more intense, and competition for talents has become the essence of international competition. The power of talents has become an important national strategy for China to face new problems and challenges. This makes the employment of college graduates more prominent. The nation relies on talents, industry relies on talents. Under such circumstances, college students shoulder more and more important responsibilities. However, in recent years, with the worldwide epidemic of the new coronavirus and the worsening economic conditions in countries around the world, many traditional industries have suffered a severe blow. Factory shutdowns, layoffs and other phenomena have occurred from time to time, causing a great impact on the employment of China's college graduates, and the pressure from all sides has become increasingly strong, so that their concept of employment has also undergone a great transformation. In recent years, people's negative psychology of employment has become increasingly serious, which fully reflects the mismatch between China's employment environment, employment orientation, employment system and college graduates. College students' psychological "signals" will have a direct impact on the employment of colleges and universities, which will in turn affect the adjustment of the national employment policy for college students [10].
Employment is the basis of people's life and development. College students play a pivotal role in country's employment. According to statistics, the number of graduates from 2022 universities will reach 10.76 million, an increase of 1.67 million over the same period last year. The employment of college students is a hot issue of current social concern. In order to ensure the employment stability of college graduates, universities have taken a series of measures to ensure the employment rate of college graduates. At this year's two sessions, the government's work report also indicated that the focus of this year's work is still on the "six stabilizers" and "six guarantees". Specifically, the employment of university graduates should be safeguarded in three aspects: first, comprehensive support for the employment of university students, that is, the early modernization of academic disciplines and professions, and their adaptation to the development trend of today's networks. High-tech talents should be trained to meet new development needs; to address the imbalance between supply and demand, supply-side employment reforms should be further deepened to promote all-round development; at the same time, they should be guided to choose their careers correctly, so as to enable them to obtain high-quality jobs, thus enabling them to play their roles to the full. Second, all parties should implement employment priority policies, strengthen labor supervision and promote a more equal employment environment. Third, flexible and new types of employment should be promoted, and trade associations should be encouraged to use digital technology to build intelligent employment data-sharing platforms to promote flexible employment for university students, and ultimately to accurately match employment supply and demand.
At present, the job search prospects of university students are bleak and the pressure of work is great, but there are still very few outstanding talents at the grass-roots level. The mentality of "aspire to the city and join the civil service" is also prevalent among college graduates looking for jobs, especially in economically better-off places, and even more so in economically better-off places. In response to the employment mentality of college students listed above, as well as the current reality of China's uneven regional development, the government has taken a variety of measures to promote college students to work in rural areas [9], and strongly support college students to work in rural areas, promote the social responsibility and sense of mission of college students, adhering to the will and determination to build the motherland. Make their own contribution to the construction of the country.
The times make young people grow and the times demand young people. College students are the more knowledgeable category of youth, is the mainstay of future development. College students should consciously take up their own historical responsibility while they are employed, have a big ambition, and closely link their employment with the development of the country. Marx, in his book "Youth's Considerations in Choosing an Occupation", elaborated on the employment philosophy of college students, pointing out that young people should adhere to the concept of "the pursuit of human happiness" and "human perfection", which are dialectically combined rather than opposing each other. Employment should not be based on selfishness, but on the well-being and development of all mankind. In their search for employment, university graduates should give full play to their talents and abilities in order to adapt to the needs of social development and actively participate in the development and construction of the country.
History has entrusted us with a mission, and the era calls for responsibility. The historical conditions and the new situation in the new era have brought new tasks to university students. At the centennial celebration of the May Fourth Movement, Xi [15] stated, "The new generation of China should cherish the times, shoulder the mission of the era, and courageously bear responsibility." In the new era, young university students must insist on applying what they learn and make sound employment choices to contribute to the construction of socialism with Chinese characteristics in the new era through practical actions [3].
The preference for 'steady progress' reflects students' alignment with the national goal of stability, demonstrating their awareness of the historical mission.
Since ancient times, the soul of patriotism has been the source of vitality for the Chinese nation. Whether in times of foreign invasion or natural disasters, the unity of the Chinese people has always prevailed. Patriotism has always been a powerful force. Xi [1] pointed out, "Patriotism is our foundation." As analyzed by Song [11], the integration of patriotic education with youth development requires a multi-dimensional approach, including ideological guidance, practical engagement, and value internalization. Contemporary youth university students must not only strengthen their cultural knowledge and technical skills but also consciously inherit the spirit of patriotism, integrating their love for the country, aspiration for strength, and dedication to national rejuvenation into the great cause of building a modern socialist country and realizing the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation [17].
For over a century, the Chinese nation has experienced countless hardships and has risen from poverty to prosperity. The Communist Party of China, closely connected to the people, has led the nation to tremendous successes. Throughout history, the fate of individuals has always been intertwined with that of the nation, and personal development is deeply tied to national rejuvenation [7]. The new era has provided university students with new opportunities and tasks, enabling them to integrate their destiny with that of the nation and society. University students must consciously abandon selfishness and prioritize collective interests, linking their personal fate with national development and the ideals of China [14].
Facing modernization and the future, the new era has provided university students with the task of character development and self-discipline. As the backbone of the country, youth must cultivate their behavior and moral character through socialist core values [3]. By grasping the new opportunities of the era, students should develop the correct worldview and values, enhancing both their soft skills and professional qualities to become pioneers, trailblazers, and devoted contributors to the era [21].
In the new era of China, the economy and society have entered a new phase, with the main social contradiction evolving into "the contradiction between people's growing needs for a better life and the unbalanced and inadequate development" [1]. The issue of university graduate employment has shifted from merely increasing employment rates to improving employment quality. University students in the new era must meet the development and practical needs of the times and contribute to realizing the "Two Centenary Goals" [15]."
In today's society, with its complexities and diversity of values, some university students still prioritize individualism and lack the sense of social responsibility expected of their peers [20]. It is essential to cultivate awareness of responsibility. Society, schools, and families must work together to enhance students' value orientation, judgment, and career attitudes. Patriotism, collectivism, and socialist consciousness should be promoted, fostering a strong sense of social responsibility and historical mission to contribute to the revitalization of socialism and the nation [6].
University graduates must not only have a strong sense of responsibility but also improve their overall competence. As socialism with Chinese characteristics enters a new era, the importance of talent resources has become increasingly evident [6]. University students, as a highly potential group in the labor market, face new demands. In today's diverse society and complex international environment, there is an urgent need for talents with innovation abilities and social adaptability [18]. However, there is a growing shortage of talent across industries. According to the "Digital Economy Employment Impact Research Report," the gap in "digital talent" in China had reached 11 million by 2020 and continues to grow [2]. To adapt to the new era's demands, university graduates must continually improve their comprehensive abilities and strive to become world-class talents to take on the responsibilities of the times [4].
Youth are the most vibrant part of society and must recognize the primary social contradictions of the new era. The new century has seen China rise from poverty to development and address the issues of the past century. However, imbalances and inadequacies in development still exist [19]. University students must understand these contradictions, make the right choices, and be willing to contribute, realizing their value through dedication [16].
With the deepening of higher education reform, the number of university graduates continues to grow, and the employment situation is less than optimistic. Against this backdrop, the psychological issues of university students have become increasingly prominent, and these issues can affect their future work and life values [12]. Through investigating the new social psychology of university students' employment choices, we can better understand their psychological characteristics and analyze employment psychology problems [13]. This research aims to promote high-quality employment for university students [6]. The social psychological analysis of university students' employment choices in the new era is as follows:
Due to policies like "Double Reduction," many people are only able to attend secondary school or vocational colleges, which gives some university students a sense of superiority [3]. They believe their qualifications are higher, leading to overly high expectations in the job search. However, their lack of experience creates a sense of disparity between their expectations and the reality of starting positions, which increases their mental pressure (Li, 2019).
Many university students believe that only by moving to large cities can they have a chance to succeed. This results in a strong aversion to rural or underdeveloped regions [6]. The excessive desire for large cities leads to talent shortages in these regions, while the demand for jobs in developed cities far exceeds supply, making positions in government and state-owned enterprises more competitive [16].
Some students rely on family connections or financial support to secure better jobs, while others face greater pressure due to average family conditions. This imbalance creates psychological instability, and some students may rely on fantasy rather than reality when seeking jobs, which leads to greater difficulties once they enter society [21].
Some university students try to start their own businesses, but due to lack of experience and market knowledge, they often fail [18]. This failure results in self-doubt and a decrease in self-esteem, leading to increased mental pressure. For graduates, the risks of entrepreneurship are high, and without mentorship or industry knowledge, most attempts are likely to fail, exacerbating their psychological stress [6].
Under the backdrop of the pandemic, employment pressures have continuously increased, and new employment-related psychological dilemmas for university students have emerged. Many students, in an attempt to avoid employment, choose to take public exams or pursue graduate studies, while others hold certain misconceptions about career choices. In this special context, integrating ideological and political education with career planning for university students, drawing on Marxist career choice theory and social psychology, can help guide students to face employment positively and correct their employment-related cognitive biases. Employment is fundamental for survival, and how to help university students secure more comprehensive and higher-quality jobs has become a critical issue in contemporary society, directly influencing the development of the entire society and the sustainable growth of the economy.
Currently, research on the employment pressures of Chinese university graduates mainly focuses on their employment pressures and coping strategies. While some progress has been made, there has been insufficient discussion on the role of career counseling services for university graduates. Surveys have shown that the satisfaction level of university students with career guidance services significantly affects their work-related stress and employment strategies. Therefore, providing more practical and up-to-date employment guidance services at the university level can reduce graduates' fear of employment, effectively lower their employment pressures, and subtly reduce the occurrence of passive employment strategies. This research, based on the theory of synergy, recognizes that university students' employment is influenced by the coordinated impact of five dimensions: the state, society, universities, families, and individuals. Based on this, the study proposes new approaches to the historical mission and employment choices of university students in the new era from a social psychological perspective, as detailed below. This integrated approach considers personal, family, school, and societal factors, forming a multi-dimensional, interactive, and complementary four-level support network that fosters a positive cycle, providing university graduates with robust and diversified support, and continuously improving the employment environment. Details are presented in Figure 3: Employment Pathways under the Social Psychological "Inner and Outer Circle System" of University Students' Employment Mentality.
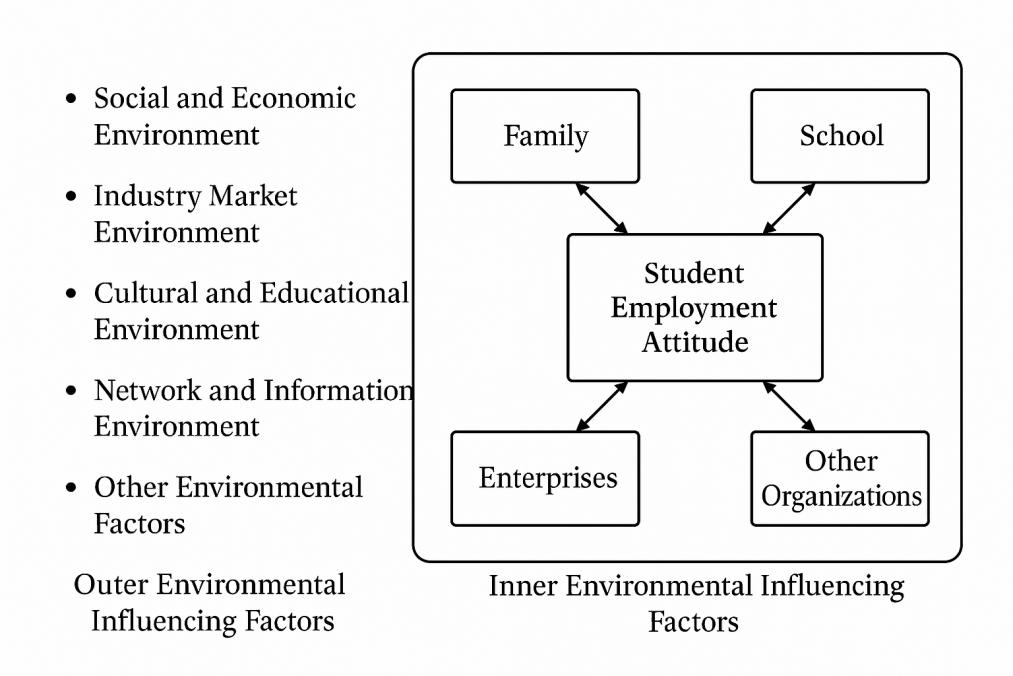
Minister of Education Chen Baosheng emphasized that the state has placed significant attention on university students' employment, proposing a "student-centered" development strategy, with an emphasis on improving employment work for students. At all levels, governments must combine "education priority" with "employment priority," coordinating efforts from the state, schools, and families to ensure a strong policy framework for prioritizing employment for university graduates.
Governments at various levels should implement an effective "prioritized" policy support system for university graduates. As emphasized by Liu [8], stabilizing employment remains a key macroeconomic goal, requiring coordinated efforts from central and local policies to expand job opportunities. Local governments must fulfill their responsibilities, ensuring that major directives and decisions from the central government regarding encouraging full employment and improving employment quality are implemented. They should establish student employment subsidies, unemployment insurance, housing benefits, and prioritized employment policies for university graduates. According to the "Employment Promotion Law," it is also crucial to "actively support university students' self-employment and entrepreneurship," maximizing the role of entrepreneurship in employment. To tackle discrimination in the job market against university graduates with insufficient internship experience, a "prioritized" employment support system for university graduates should be developed.
University student employment is a key issue for both the Party and the state. To achieve high-quality and comprehensive employment for university graduates, it is necessary to construct a "precision" dynamic support mechanism. This system involves cooperation between local governments, universities, and businesses to expand employment opportunities and provide continuous support for graduates.
Universities should build a dynamic support network involving "government-university-business" relationships. First, governments must play their part in increasing job opportunities. Second, universities must develop "precision" dynamic employment support systems to provide comprehensive assistance for students and the unemployed. Finally, businesses should establish "precision" flexible collaborative support systems, tailored to meet specific needs, achieving mutual benefit.
University graduates should proactively understand the current employment situation, employment channels, and policies, and consider their strengths and weaknesses to choose careers that align with their personal development. They should make career plans early and adjust their mindset to explore new employment trends, especially regarding flexible employment, insufficient employment, and entrepreneurship, avoiding rigid thinking tied to traditional employment models. Graduates can also contribute to national development by working in grassroots areas, in line with national policies.
In the post-epidemic period, the economic structure of the world has undergone tremendous changes, and is experiencing huge changes rarely seen in a century, which have had a profound impact on the global industrial landscape, and also on the job market. Coupled with the fact that college students who have just entered the society are not very clear about the unspoken rules of the society, they are under great pressure to work. Therefore, the employment service departments of colleges and universities should make appropriate preparations according to the needs of the labor market in order to understand the current employment situation of college students and the possible psychological impacts. Colleges and universities will work together with college students' psychological counseling centers and employment centers to carry out psychological counseling on employment and formulate corresponding countermeasures for their specific situations. An early warning system for psychological stress in employment will be set up for "schools, faculties, majors and classes", and relevant departments at all levels will form "point-to-point" teams to deal with psychological problems in employment. The relevant departments at all levels will form a "point-to-point" team to deal with employment psychological problems, establish a hierarchical reporting system for common employment psychological problems, highlight "personalization", and intervene in a timely manner, so as to establish a mechanism for preventing psychological problems among college students. In the practice of employment of college graduates, it is important to be targeted, targeted and targeted. Through the "point to point" psychological counseling, we can maximize the needs of college students.
Entering the new era, changes in economic and social factors have put forward higher requirements for the employment of today's college graduates. At the same time, because of their own perception is not clear, ability and job requirements do not match, not strong practical ability and so on, college students in the post-graduation choice of work often produce difficult to choose a job, difficult to employ, difficult to work and so on, resulting in a certain degree of resistance to employment. Therefore, after entering the university, college students should balance the relationship between academics and employment in time, find the focus between the two, grasp both theory and practice, make employment planning and life direction choice as early as possible, and enhance their professional ability to refine themselves and adapt to the labor market requirements. In addition, you can also use the relevant resources to learn the relevant industry knowledge, its in the era of information at your fingertips, it is more important to make good use of online resources to enhance their own. At the same time, they should not only focus on learning but also neglect practice, such as using the summer and winter vacations to participate in internships and social practice to improve their skills. In addition, college students should also establish the concept of "learning by competition", and take the initiative to participate in relevant competitions organized by the school, such as the college students' "Internet +" competition, relevant vocational skills competitions, academic competitions, etc., which is also an effective approach to enhance their own ability, find their own advantages and improve their own deficiencies. It is also an effective approach to enhance their abilities, find their own strengths and improve their own deficiencies. Universities should establish a set of dynamic support mechanisms for "difficult to employ" in accordance with their own characteristics. First of all, special employment departments should be set up within the university to carry out off-campus and on-campus cooperation. Inter-university cooperation mainly focuses on learning and sharing employment psychology database, which provides new ideas for solving the employment problem of college students. Secondly, the cooperation between universities and second-level colleges mainly focuses on the establishment of dynamic files of students with difficulties in employment, which can make better use of the professional organizations of the second-level colleges to help students in a more "precise" way. The employment departments of the second-level colleges should establish a precise and dynamic help system according to the requirements of the university, and provide personalized, targeted and whole-process tracking and feedback to graduates. Fourthly, we should strengthen the collaboration between schools, colleges and universities, and improve the working mechanism for graduates who are "difficult to employ". From the aspects of employment guidance, psychological problems, policies, funds, etc., to establish "difficult to employ" college students employment guidance, psychological counseling, policy support and other aspects of accurate help, to provide policy support for "difficult to employ" college students.
Establishing a mechanism for cooperation between families and schools, activating the synergy between them and jointly promoting the implementation of a "prioritized" policy and guarantee system for the provision of university graduates. The solution to the employment problem of college students requires the joint efforts of all parties, paying attention to the influence of family factors on college students. First of all, we should establish the concept of "family and school" to promote employment; families, colleges and universities should establish the idea of employment first, guide and instruct college graduates to formulate their own career planning and vocational planning; colleges and universities and families should make full use of their own advantages, from a variety of aspects of college students career education, so that they form the correct concept of employment. concept of employment. Secondly, it is necessary to improve the flexible collaboration mechanism that prioritizes employment in families and schools. The psychological problems of college students' employment is the main body of the university, with college students as the leading guide to deal with the psychological problems of college students' employment; during the period of college students' leaving school, the mental health problems of college students should be solved by the family, and the two are organically combined. In the whole process of cultivating students, schools and parents find out the reasons for students' employment difficulties in time, so as to understand the reasons more comprehensively and deeply, and make inspired communication to realize real-time feedback and give support. On this basis, measures are proposed to strengthen communication and communication between families and schools. The establishment of career development and vocational education files of college students and parents, regular communication and counseling among parents, students and colleges and universities, in order to promote the diversification of parents, students and colleges and universities, the form of home-school cooperation, broaden the content of home-school cooperation, and broaden the channels of cooperation between mothers and schools. The comprehensive effect of the "Three Links" should be brought into full play, so that graduates can be employed earlier and in a more comprehensive and better quality. Family is an important factor in the growth of college students, and a good family environment has a great influence on the growth of college students. And many college students are largely influenced by family factors when choosing specific careers and workplaces. For example, some college students choose employment because of family economic conditions or parents do not support graduate school and give up graduate school; some college students are more attached to their families, so they are attached to their families and choose to work in cities close to their homes; parents' occupations will also affect college students' employment choices, if their parents think that their own occupations are well-paid and thus often praised, in a sense, this will make college students prioritize the industry when choosing a job, and college students should be more careful when making employment choices, and should be more careful when making employment choices. When choosing employment, students should consider more from the perspective of their own development, and make choices after a full understanding of the chosen occupation, and do not pay too much attention to the influence of family factors and thus ignore their own preferences. At the same time, college students should communicate with their parents after making career plans, so that they can understand their own plans for the future, and selectively adopt the advice given by their parents, so that on the one hand, they can get better support from their parents, and on the other hand, they can also reduce their own detours. Parents should also respect the choice of college students from a reasonable range of advice, but not to take the way of coercion, otherwise it is easy to counterproductive.
Under the current pandemic, university students face increasing employment pressures, and new psychological dilemmas are emerging. Many students turn to graduate school or civil service exams to avoid immediate employment challenges, while others have misconceptions about career choices. In this context, combining ideological education with career planning, integrating Marxist career choice theory and social psychology, can effectively guide students to face employment opportunities positively and correct cognitive biases related to employment. This research, based on synergy theory, proposes new approaches to university students' historical mission and employment choices from a social psychological perspective, incorporating contributions from the state, society, universities, and families. These four aspects should be integrated into a multi-dimensional, interactive, and cooperative support network to improve the employment environment continuously.
IECE Transactions on Social Statistics and Computing
ISSN: 2996-8488 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/iece/