Abstract
Farmers sometimes grow crops with low yields, wasting land, labor, and time—especially in developing countries where demand for food is increasing. A Crop Recommendation System (CRS) can help by using precision farming techniques that analyze soil and environmental data to suggest the most suitable crops. This study proposes a CRS using a Modified Salp Swarm Algorithm (MSSA) for feature selection and an Adaptive Weighted Bi-directional Long Short-Term Memory (AWBiLSTM) ensemble for prediction. MSSA enhances the original algorithm by improving local search and convergence speed, addressing SSA’s limitations. Climate data is pre-processed and relevant features are selected using MSSA. AWBiLSTM then predicts suitable crops with improved accuracy. Experimental results show that the MSSA-AWBiLSTM approach outperforms existing methods in precision, recall, and execution time. The proposed method obtains an accuracy of 98.72%, precision of 98.81%, recall of 98.54%, specificity of 98.10%, PR-Score of 98.18%, ROC-Score of 98.49%, F1-Score of 98.48%, and Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC) of 97.63%.
Keywords
soil and climate conditions
feature Selection
crop recommendation
modified salp swarm algorithm
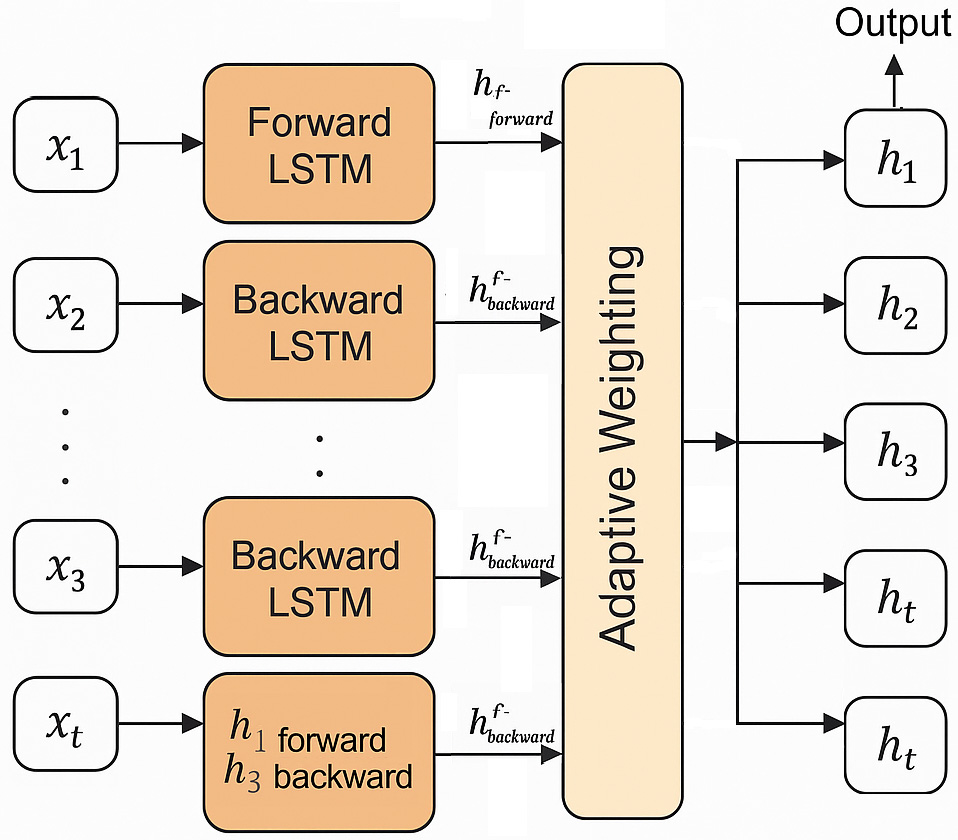
adaptive weighting based BiLSTM
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Majumdar, P. (2025). Modified Salp Swarm Algorithm with Adaptive Weighting Based Bidirectional LSTM Network Ensemble Method for Crop Recommendation. IECE Transactions on Swarm and Evolutionary Learning, 1(1), 3–11. https://doi.org/10.62762/TSEL.2025.947593
Publisher's Note
IECE stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Emerging and Computer Engineers (IECE) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue